Bonsai Trees
Styles

When styling and designing a bonsai it is important to look closely at the tree and examine the different possibilities that present themselves. Decide first whether you are trying to create a young, old or ancient tree and let the tree help you determine what your objectives should be.
Remember that you are unlikely to achieve a convincing aged looking tree from a five year old sapling. Young trees in the wild tend to have upward growing branches, whereas the branches of older trees will have been pulled downwards over the years, as a result of the extra weight of their branches and foliage.
In most cases the tree will help you choose the style and you should not approach the potential bonsai with fixed ideas. For example, you cannot create a formal upright bonsai from a tree with a curved trunk. Do bear in mind that bonsai rules in general are for guidance only and do not necessarily have to be strictly adhered to. Look to nature for inspiration, as bonsai styles have not been invented, but actually recreate the ways that different trees grow in their natural environments.
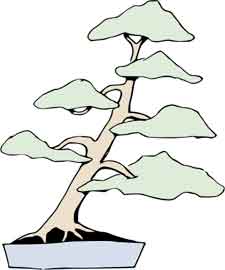
Formal Upright - Chokkan
Informal Upright - Moyogi
Literati - Bunjingi
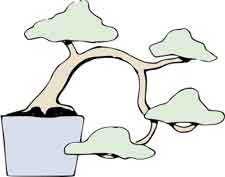
Windswept - Fukinagashi
Cascade - Kengai
Twin Trunk - Sokan
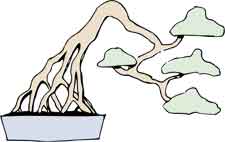
Root Over Rock - Sekijoju
Bonsai Root On Rock - Ishitsuki
Bonsai Driftwood - Sharimiki
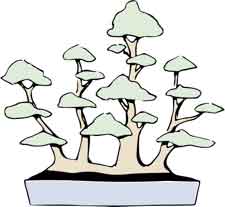
Bonsai Group Planting - Yose-Ue
Bonsai Broom - Hokidachi
Other popular bonsai styles include:
- Slanting - trunk leaning to one side, with branches on both sides - apex to one side of the base
- Semi Cascade - growing in a gentle downwards and horizontal direction, but not below the base of the pot
- Triple Trunk - tree with three trunks, usually originating at soil level
- Clump - several trunks grow from the roots of one tree, creating a small woodland effect
- Raft - tree lying on its side with branches growing from the trunk to form a group of trees
- Weeping - informal upright tree with branches weeping vertically - usual willow, birch or tamarix
- Candle Flame - upwards branches form a flame shape - typically associated with ginkgos
- Two Tree - two separate trees planted close together, resembling a twin trunk
- Octopus - multi-trunk variant with many twisted trunks - usually pines
- Split Trunk - trunk has been literally split to form separate elements
- Exposed Root - base of trunk is formed by heavy, woody, exposed roots
- Twisted Trunk - trunk that appears to twist and spiral - often seen with pomegranates
- Coiled Trunk - grotesque, with severe bends in the trunk
- Landscape - group of trees planted with rocks to form a realistic miniature landscape
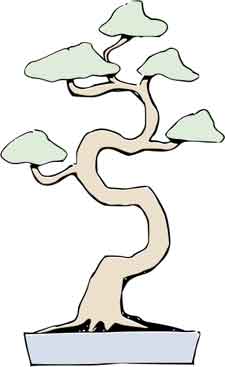
 When styling and designing a bonsai it is important to look closely at the tree and examine the different possibilities that present themselves. Decide first whether you are trying to create a young, old or ancient tree and let the tree help you determine what your objectives should be.
When styling and designing a bonsai it is important to look closely at the tree and examine the different possibilities that present themselves. Decide first whether you are trying to create a young, old or ancient tree and let the tree help you determine what your objectives should be.



